Introduction and Background
In the rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, hospital administration stands as the linchpin of effective healthcare delivery. While traditionally focused on logistical and financial operations, modern hospital administration is increasingly concerned with optimizing patient outcomes through innovative strategies and tools. Among these, telehealth nursing has emerged as a transformative approach, offering new avenues to enhance patient care, particularly in the context of remote monitoring, chronic disease management, and improved access to specialized nursing expertise. This review delves into the critical intersection of hospital administration and telehealth nursing, exploring how effective administrative practices can leverage Telehealth Nursing Tools And Strategies For Optimal Patient Care Doi.
Hospital administrators are tasked with overseeing complex systems, from resource allocation and financial sustainability to quality improvement and patient safety [1]. The integration of telehealth nursing into hospital operations represents a significant shift, requiring administrators to understand and implement new technologies, workflows, and training programs. The ultimate aim remains consistent: to improve patient outcomes, encompassing not only clinical effectiveness but also patient satisfaction, safety, and overall well-being [3]. Telehealth nursing, with its capacity to extend care beyond hospital walls, offers a powerful means to achieve these goals, aligning perfectly with the evolving focus on patient-centered and value-based healthcare models.
This comprehensive review aims to explore the multifaceted role of hospital administration in effectively integrating and utilizing telehealth nursing tools and strategies for optimal patient care doi. We will examine key administrative components, strategies for implementation, measurement methodologies, and future trends, all within the framework of leveraging telehealth nursing to enhance patient outcomes. By highlighting the synergistic relationship between hospital administration and telehealth nursing, we aim to provide a roadmap for healthcare institutions seeking to optimize patient care in the digital age.
Review
Key Components of Effective Hospital Administration in the Age of Telehealth Nursing
Leadership and Governance for Telehealth Integration
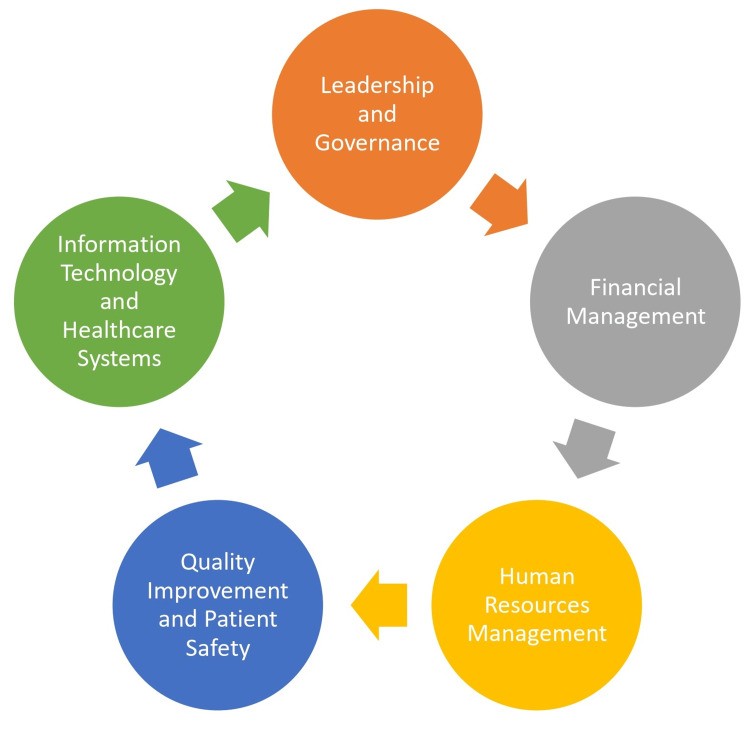
Effective leadership and governance are paramount for successfully integrating telehealth nursing into hospital operations and realizing its potential to enhance patient outcomes. Hospital administrators, CEOs, and nursing leadership play crucial roles in championing telehealth initiatives, setting the strategic direction, and fostering a culture that embraces digital innovation in nursing practice [4]. Figure 1 illustrates the key components of effective hospital administration, now viewed through the lens of telehealth integration.
Figure 1. Key components of effective hospital administration integrating telehealth nursing.
Alt text: Diagram illustrating key components of effective hospital administration, emphasizing the integration of telehealth nursing, including leadership, financial management, HR, quality improvement, IT, and patient-centered care, all converging to improve patient outcomes.
Hospital leadership’s commitment to telehealth nursing tools and strategies for optimal patient care doi is vital. Leaders must articulate a clear vision for telehealth, emphasizing its benefits for patients and staff. Their leadership style should encourage innovation and empower nursing teams to adopt and adapt telehealth solutions. This involves providing resources for training, technology infrastructure, and ongoing support for telehealth programs. Effective leadership also includes establishing clear governance structures for telehealth, defining roles and responsibilities, and ensuring accountability for telehealth program outcomes [5].
Governance structures are crucial for managing the unique risks and opportunities associated with telehealth nursing. This includes addressing data security and patient privacy concerns related to remote patient monitoring and virtual consultations. Clear policies and procedures must be in place to ensure compliance with regulations such as HIPAA and to maintain ethical standards in telehealth practice. Governance frameworks should also support adaptability, allowing hospitals to respond to evolving telehealth technologies and patient needs. For instance, a telehealth committee can be established as part of the governance structure to oversee telehealth strategy, monitor program performance, and address ethical and risk management issues specific to telehealth nursing services [6].
Ethical considerations are particularly important in telehealth nursing. Issues such as digital access equity, ensuring informed consent in virtual settings, and maintaining patient confidentiality across digital platforms require careful consideration. Hospital administrators must ensure that telehealth nursing programs are implemented ethically, respecting patient autonomy, promoting beneficence, preventing harm, and ensuring justice in access to telehealth services. Ethical leadership in this context includes promoting cultural competency in telehealth delivery and addressing potential biases in algorithms used in telehealth tools [7].
Financial Management for Telehealth Nursing Programs
Financial management is a critical enabler of successful telehealth nursing programs. Hospital administrators must strategically allocate resources to support telehealth infrastructure, technology, and personnel, demonstrating the cost-effectiveness and return on investment of telehealth nursing tools and strategies for optimal patient care doi [8]. This requires a shift in financial planning to incorporate telehealth as a core component of patient care delivery.
Budgeting and resource allocation for telehealth nursing require careful planning. Administrators need to invest in telehealth platforms, secure communication systems, remote monitoring devices, and training for nursing staff. Strategic budgeting involves prioritizing telehealth investments that align with the hospital’s strategic goals and patient needs. For example, if a hospital aims to reduce readmission rates for heart failure patients, investing in remote patient monitoring programs facilitated by telehealth nurses would be a strategic resource allocation. Demonstrating the financial benefits of telehealth, such as reduced hospitalizations and improved efficiency, is crucial for securing continued investment [9].
Cost-effectiveness and financial sustainability are key considerations for telehealth nursing programs. While initial investments are necessary, telehealth can offer long-term cost savings by reducing hospital readmissions, emergency department visits, and length of stay. Telehealth nursing can also improve efficiency by enabling nurses to manage larger patient panels remotely and by streamlining workflows through digital tools. Administrators should conduct thorough cost-benefit analyses to demonstrate the financial value of telehealth nursing and to identify strategies for maximizing its cost-effectiveness. This may include optimizing telehealth workflows, negotiating favorable contracts with telehealth technology vendors, and leveraging reimbursement models that support telehealth services [10].
Revenue generation and reimbursement for telehealth nursing services are evolving areas. Administrators must navigate complex reimbursement landscapes, understanding payer policies for telehealth services, including Medicare, Medicaid, and private insurers. Maximizing revenue while ensuring ethical billing practices for telehealth nursing is crucial for program sustainability. This involves staying informed about changes in telehealth reimbursement policies, optimizing billing processes for telehealth services, and potentially exploring new revenue streams through expanded telehealth offerings, such as virtual chronic disease management programs or remote specialty nursing consultations [11].
Human Resources Management for Telehealth Nursing Workforce
Human resource management is essential for building and supporting a competent and engaged telehealth nursing workforce. Hospital administrators must adapt HR strategies to recruit, train, and retain nurses skilled in utilizing telehealth nursing tools and strategies for optimal patient care doi [12]. This requires a proactive approach to workforce planning and development in the telehealth domain.
Staffing and workforce planning for telehealth nursing involves determining the optimal mix of telehealth nurses, support staff, and technology specialists. Administrators need to consider patient demographics, telehealth service volume, and the complexity of telehealth interventions when planning telehealth nursing staffing levels. Strategic workforce planning also includes forecasting future telehealth nursing needs, anticipating the growth of telehealth services and the evolving skill sets required for telehealth nursing practice. This may involve creating new telehealth nursing roles, such as telehealth nurse coordinators or telehealth nurse specialists, and developing career pathways for nurses in telehealth [13].
Training and development are critical for equipping nurses with the skills to effectively utilize telehealth technologies and deliver virtual care. Comprehensive training programs should cover telehealth platforms, remote patient monitoring devices, virtual communication skills, and telehealth-specific clinical protocols. Ongoing professional development is necessary to keep telehealth nurses updated on the latest telehealth technologies, best practices, and regulatory changes. Administrators should invest in specialized telehealth nursing training programs, simulation-based telehealth training, and mentorship opportunities to support the development of a proficient telehealth nursing workforce [14].
Employee satisfaction and retention are vital in telehealth nursing, just as in traditional nursing roles. Hospital administrators must create a supportive and engaging work environment for telehealth nurses, addressing the unique challenges and rewards of virtual nursing practice. This includes providing adequate technical support, fostering a sense of community among telehealth nurses, offering flexible work arrangements, and recognizing the contributions of telehealth nursing to patient care. Addressing potential feelings of isolation among remote telehealth nurses and ensuring work-life balance are important aspects of promoting telehealth nurse satisfaction and retention [15].
Quality Improvement and Patient Safety in Telehealth Nursing
Quality improvement and patient safety are paramount in telehealth nursing. Hospital administrators are responsible for implementing robust quality metrics, patient safety protocols, and continuous improvement methodologies to ensure the safe and effective delivery of telehealth nursing tools and strategies for optimal patient care doi [16]. This requires adapting traditional quality improvement frameworks to the virtual care context.
Quality metrics and measurement in telehealth nursing need to be tailored to capture the unique aspects of virtual care delivery. Key metrics may include telehealth consultation wait times, patient satisfaction with telehealth encounters, telehealth technology usability, telehealth nurse response times, and clinical outcomes achieved through telehealth interventions (e.g., blood pressure control in remote hypertension management programs). Administrators should establish comprehensive performance measurement systems to monitor these telehealth-specific quality metrics and to track the impact of telehealth nursing on overall patient outcomes. Data from telehealth platforms, patient satisfaction surveys, and clinical outcome databases should be used to inform quality improvement efforts [17].
Patient safety protocols and initiatives must be adapted for the telehealth environment. This includes developing protocols for virtual patient assessment, remote medication reconciliation, managing emergencies in telehealth settings, and ensuring data security and patient privacy during telehealth interactions. Administrators should implement telehealth-specific patient safety initiatives, such as virtual fall risk assessments, remote monitoring protocols to detect early signs of patient deterioration, and telehealth-based medication safety education programs. Regular audits of telehealth practices and incident reporting systems should be in place to identify and address potential safety risks in telehealth nursing [18].
Continuous improvement methodologies are essential for optimizing telehealth nursing services. Hospitals should apply methodologies like PDSA cycles or Lean Six Sigma to telehealth workflows, processes, and technologies. Administrators should foster a culture of continuous quality improvement in telehealth nursing, encouraging telehealth teams to identify areas for improvement, implement evidence-based practices, and use data to drive ongoing enhancements. This may involve streamlining telehealth workflows, improving telehealth technology usability, and refining telehealth nursing protocols based on performance data and patient feedback [19].
Information Technology and Healthcare Systems for Telehealth Nursing
Electronic health records (EHR) and health information systems are foundational for effective telehealth nursing. Hospital administrators must ensure seamless integration of telehealth platforms and data with existing EHR systems to facilitate comprehensive patient care and data management. This integration is crucial for leveraging telehealth nursing tools and strategies for optimal patient care doi [20].
EHR integration with telehealth systems enables telehealth nurses to access complete patient medical histories, document virtual encounters directly into the EHR, and share telehealth data with other members of the care team. Administrators should prioritize EHR integration when selecting telehealth platforms and ensure that telehealth systems are interoperable with the hospital’s EHR infrastructure. This integration streamlines workflows, reduces data duplication, and enhances care coordination. Proper training for telehealth nurses on EHR use within the telehealth context is also essential [36].
Telemedicine and healthcare technology trends are rapidly shaping telehealth nursing. Administrators must stay abreast of emerging technologies, such as AI-powered telehealth tools, wearable remote monitoring devices, and virtual reality applications for nursing education and patient engagement. Leveraging these technologies can enhance the capabilities of telehealth nursing and expand the scope of virtual care delivery. For example, AI-powered tools can assist telehealth nurses in remote patient assessment and risk stratification, while wearable devices can provide continuous physiological data for remote monitoring. Strategic adoption of relevant healthcare technologies is crucial for advancing telehealth nursing services [21].
Data analytics and decision support systems are increasingly important for optimizing telehealth nursing programs. Administrators should utilize data analytics to monitor telehealth program performance, identify trends in telehealth utilization, and evaluate the impact of telehealth nursing interventions on patient outcomes. Decision support systems, integrated with telehealth platforms, can provide telehealth nurses with real-time alerts, clinical guidelines, and patient-specific recommendations during virtual encounters. Data-driven decision-making is essential for continuously improving telehealth nursing services and demonstrating their value to the organization and patients [22].
Strategies for Improving Patient Outcomes through Telehealth Nursing
Patient-centered care is at the heart of effective telehealth nursing. Telehealth offers unique opportunities to personalize care, improve patient access, and enhance patient engagement, aligning perfectly with the principles of telehealth nursing tools and strategies for optimal patient care doi. Table 1 outlines key strategies for improving patient outcomes, specifically considering the role of telehealth nursing.
Table 1. Strategies for Improving Patient Outcomes with Telehealth Nursing Integration.
| Strategy | Description | Telehealth Nursing Application |
|---|---|---|
| Patient-Centered Care | Tailoring care to individual needs and preferences, enhancing satisfaction and engagement. | Virtual care plans tailored to patient needs, remote monitoring of patient-reported outcomes, telehealth-based patient education. |
| Collaboration and Interdisciplinary Care | Promoting teamwork among healthcare professionals for comprehensive care. | Virtual interdisciplinary team meetings, telehealth consultations with specialists, secure messaging for care coordination. |
| Measurement and Evaluation | Using KPIs and data analysis to monitor outcomes and drive quality improvement. | Telehealth-specific KPIs (virtual visit wait times, telehealth satisfaction), outcome tracking for telehealth interventions, data analytics to optimize telehealth programs. |
| Future Trends and Challenges | Adapting to emerging technologies and evolving healthcare policies in telehealth. | Integration of AI in telehealth nursing, addressing digital health equity, navigating evolving telehealth regulations. |
Telehealth nursing excels at enhancing patient-centeredness by providing convenient, accessible care that fits into patients’ lives. Virtual visits eliminate travel barriers, reduce wait times, and allow patients to receive care in the comfort of their homes. Telehealth nurses can use virtual communication tools to build strong patient-provider relationships, provide personalized education and support, and empower patients to actively participate in their care. Remote patient monitoring, facilitated by telehealth nurses, allows for continuous tracking of patient health data, enabling proactive interventions and personalized care adjustments. Strategies for enhancing patient satisfaction in telehealth nursing include ensuring ease of use of telehealth technology, providing clear instructions for virtual visits, and offering multiple telehealth communication modalities (e.g., video, phone, secure messaging) to cater to patient preferences [23–28].
Collaboration and interdisciplinary care are enhanced through telehealth nursing. Virtual platforms facilitate communication and collaboration among nurses, physicians, specialists, and other members of the care team, regardless of location. Telehealth nurses can participate in virtual interdisciplinary team meetings, share patient data securely, and coordinate care plans across different providers. Telehealth consultations with specialists can be efficiently arranged, improving access to specialized expertise for patients in remote or underserved areas. Standardized telehealth communication protocols and secure messaging systems further enhance interdisciplinary collaboration in telehealth nursing [25].
Measurement and Evaluation of Telehealth Nursing Outcomes
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Telehealth Nursing Outcomes
Specific KPIs are needed to evaluate the effectiveness of telehealth nursing tools and strategies for optimal patient care doi. These KPIs should capture the unique aspects of telehealth nursing and their impact on patient outcomes.
- Telehealth consultation access metrics: Measuring wait times for virtual appointments and the percentage of patients accessing telehealth services can indicate the accessibility and efficiency of telehealth nursing programs. Targets for wait times and access rates should be established and monitored to ensure timely access to virtual nursing care [29].
- Patient satisfaction with telehealth nursing: Specific patient satisfaction surveys focused on telehealth encounters should be used to assess patient experience with virtual nursing care. These surveys should capture aspects such as telehealth technology usability, nurse communication skills in virtual settings, and overall satisfaction with telehealth services. Regularly monitoring patient satisfaction scores and addressing areas for improvement is crucial [24].
- Clinical outcomes achieved through telehealth nursing: Outcome metrics relevant to the specific telehealth nursing interventions should be tracked. For example, for remote chronic disease management programs, KPIs might include blood pressure control rates, HbA1c levels, and medication adherence rates. For telehealth-based post-discharge follow-up, readmission rates and emergency department revisit rates are relevant KPIs [30].
- Telehealth technology usability and adoption rates: Metrics related to the ease of use and adoption of telehealth technology by both nurses and patients are important. This may include measuring telehealth platform usage rates, technical support requests related to telehealth, and nurse proficiency in using telehealth tools. Improving telehealth technology usability and providing adequate training can enhance adoption rates [31].
- Cost-effectiveness of telehealth nursing programs: Analyzing the financial impact of telehealth nursing programs, including cost savings from reduced hospitalizations, emergency department visits, and travel costs, is crucial for demonstrating the value of telehealth investments. Return on investment (ROI) calculations and cost-benefit analyses should be conducted to assess the economic value of telehealth nursing [32].
- Nurse satisfaction and burnout in telehealth nursing: Monitoring nurse satisfaction, burnout rates, and turnover rates among telehealth nurses is important for ensuring workforce well-being and program sustainability. Regular surveys and feedback mechanisms can help assess telehealth nurse satisfaction and identify factors contributing to burnout. Strategies to support telehealth nurse well-being are essential [33].
- Adherence to telehealth nursing protocols and guidelines: Measuring adherence to established telehealth nursing protocols and clinical guidelines ensures consistent and quality virtual care delivery. Regular audits of telehealth nursing practice and feedback mechanisms can be used to monitor protocol adherence and drive continuous improvement [35].
Data Collection and Analysis for Telehealth Nursing Evaluation
Robust data collection and analysis are essential for evaluating telehealth nursing programs and demonstrating the value of telehealth nursing tools and strategies for optimal patient care doi.
- Telehealth platform data: Telehealth platforms themselves generate valuable data on telehealth encounters, including visit duration, communication modalities used, patient demographics, and clinical data collected during virtual visits. Administrators should leverage telehealth platform data for performance monitoring and quality improvement [36].
- EHR data integration for telehealth outcomes: Integrating telehealth data with EHR systems allows for comprehensive outcome tracking. EHR data can be used to analyze the impact of telehealth nursing on clinical outcomes, utilization metrics (e.g., readmissions), and patient safety indicators. Data integration is crucial for a holistic evaluation of telehealth nursing [37].
- Patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in telehealth: Collecting PROs through telehealth platforms or integrated surveys can provide valuable insights into patient experience, quality of life, and functional status following telehealth nursing interventions. PRO data can complement clinical outcome measures and provide a more patient-centered evaluation of telehealth nursing effectiveness [34].
- Qualitative data from telehealth nurse and patient feedback: Collecting qualitative data through surveys, interviews, or focus groups with telehealth nurses and patients can provide rich insights into the strengths and weaknesses of telehealth nursing programs, identify areas for improvement, and capture the nuanced experiences of virtual care. Qualitative data complements quantitative metrics and provides a deeper understanding of telehealth nursing impact [38].
- Advanced analytics for telehealth data: Employing advanced analytics techniques, such as predictive modeling and machine learning, on telehealth data can identify patterns, predict patient risks, and optimize telehealth interventions. Data mining and machine learning can uncover valuable insights from telehealth data to further enhance the effectiveness of telehealth nursing programs [39].
- Real-time dashboards for telehealth monitoring: Implementing real-time dashboards that visualize key telehealth KPIs allows administrators and telehealth teams to monitor program performance in real-time, identify potential issues proactively, and make timely adjustments to improve telehealth service delivery [41].
Benchmarking and Comparing Telehealth Nursing Performance
Benchmarking telehealth nursing performance against peer institutions and national standards is essential for identifying best practices and driving continuous improvement in telehealth nursing tools and strategies for optimal patient care doi.
- Peer benchmarking for telehealth programs: Comparing telehealth nursing KPIs with similar hospitals or healthcare systems that have established telehealth programs provides valuable insights into relative performance and identifies areas for improvement. Participating in telehealth benchmarking initiatives and data-sharing agreements with peer institutions can facilitate mutual learning and quality enhancement [42].
- National telehealth benchmarks and guidelines: Benchmarking against national telehealth benchmarks and guidelines established by professional organizations or regulatory bodies provides a broader perspective on telehealth nursing performance and ensures alignment with industry standards. Utilizing publicly available telehealth performance data and adhering to national telehealth guidelines can guide quality improvement efforts [43].
- Internal benchmarking of telehealth nursing services: Comparing performance across different telehealth nursing service lines or telehealth teams within the hospital system can identify best practices within the organization and facilitate internal knowledge sharing. Internal benchmarking can promote consistency and high standards across all telehealth nursing services [16].
- Collaborative telehealth networks for data sharing: Participating in collaborative telehealth networks that share data and best practices among member organizations can accelerate learning and improvement in telehealth nursing. Collaborative networks provide a platform for sharing challenges, successes, and innovative approaches to telehealth nursing [44].
- Continuous benchmarking and performance monitoring: Regularly updating and reviewing benchmarking data is essential for tracking progress in telehealth nursing program improvement and adapting strategies based on performance trends and evolving best practices. Continuous monitoring of benchmarked telehealth KPIs ensures ongoing quality enhancement [16].
Future Trends and Challenges in Telehealth Nursing Administration
Emerging Technologies in Telehealth Nursing Administration
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in telehealth nursing: AI and machine learning are poised to revolutionize telehealth nursing administration. AI-powered tools can automate telehealth scheduling, triage virtual patient requests, provide virtual nursing assistants for patient education and support, and analyze telehealth data to predict patient risks and personalize virtual care interventions. Administrators should explore AI applications to enhance telehealth nursing efficiency, scalability, and effectiveness [45].
- Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) in telehealth nursing: VR and AR technologies offer immersive experiences for telehealth nursing education, patient engagement, and virtual home visits. VR simulations can train telehealth nurses in virtual patient assessment and communication skills. AR applications can guide patients through self-care procedures at home under remote nursing guidance. Administrators should consider incorporating VR/AR into telehealth nursing programs to enhance training and patient care [46].
- Wearable sensors and remote physiological monitoring: The proliferation of wearable sensors and remote monitoring devices expands the capabilities of telehealth nursing. Administrators should invest in integrating wearable data streams into telehealth platforms, enabling continuous remote monitoring of vital signs, activity levels, and other physiological parameters. This real-time data can empower telehealth nurses to proactively manage chronic conditions, detect early signs of deterioration, and personalize interventions [47].
- Blockchain for telehealth data security and interoperability: Blockchain technology can enhance the security and interoperability of telehealth data. Administrators should explore blockchain applications for secure patient data sharing in telehealth networks, patient consent management, and streamlined telehealth billing and reimbursement processes. Blockchain can address data privacy and security concerns in telehealth and facilitate interoperability across telehealth systems [48].
- Internet of Things (IoT) in telehealth nursing: The IoT connects medical devices, sensors, and telehealth platforms, enabling seamless data exchange and remote management. Administrators should leverage IoT solutions to create smart telehealth environments, optimize telehealth workflows, and enhance remote patient monitoring capabilities. IoT can improve telehealth nursing efficiency and data integration [49].
Evolving Healthcare Policies and Regulations for Telehealth Nursing
- Telehealth reimbursement policy changes: Evolving reimbursement policies for telehealth services significantly impact the financial sustainability of telehealth nursing programs. Administrators must stay informed about changes in Medicare, Medicaid, and private payer telehealth reimbursement policies and adapt telehealth billing practices accordingly. Advocating for favorable telehealth reimbursement policies is crucial for program viability [51].
- Licensure and regulatory issues for telehealth nursing across state lines: Navigating varying state licensure requirements and regulations for telehealth nursing practice across state lines presents a challenge. Administrators should monitor interstate telehealth licensure compacts and advocate for policies that facilitate telehealth nursing practice across state borders while ensuring patient safety and regulatory compliance [52].
- Data privacy and security regulations for telehealth: Stringent data privacy and security regulations, such as HIPAA, apply to telehealth data. Administrators must ensure that telehealth nursing programs comply with all relevant data privacy and security regulations, implementing robust cybersecurity measures and data protection protocols to safeguard patient information in virtual care settings [53].
- Digital health equity and access to telehealth nursing: Addressing digital health equity and ensuring access to telehealth nursing services for all patient populations, including underserved communities and those with limited digital literacy, is a growing policy imperative. Administrators should implement strategies to bridge the digital divide, providing technology assistance and culturally tailored telehealth services to promote equitable access to telehealth nursing [55].
- Integration of telehealth nursing into value-based care models: The shift towards value-based care models necessitates integrating telehealth nursing into these models to demonstrate its value in improving patient outcomes and reducing costs. Administrators should align telehealth nursing programs with value-based care initiatives, tracking outcome metrics relevant to value-based contracts and demonstrating the contribution of telehealth nursing to achieving value-based care goals [53].
Potential Obstacles and Strategies to Address Them in Telehealth Nursing
- Technology adoption barriers among nurses and patients: Resistance to technology adoption among some nurses and patients can hinder telehealth nursing implementation. Strategies to address this include providing user-friendly telehealth platforms, offering comprehensive training and technical support, and demonstrating the benefits of telehealth to both nurses and patients. Change management strategies and addressing technology anxiety are important [56].
- Interoperability challenges between telehealth systems and EHRs: Lack of seamless interoperability between telehealth platforms and EHR systems can create workflow inefficiencies and data silos. Advocating for standardized data formats and interoperable telehealth systems, and working with EHR vendors to improve telehealth integration, are crucial steps to address interoperability challenges [58].
- Cybersecurity threats to telehealth data and systems: Telehealth systems are vulnerable to cybersecurity threats, requiring robust security measures to protect patient data and ensure system integrity. Investing in cybersecurity infrastructure, implementing strong encryption and access controls, and providing cybersecurity training to telehealth staff are essential to mitigate cybersecurity risks [59].
- Maintaining patient engagement and rapport in virtual settings: Building and maintaining patient engagement and rapport in virtual telehealth encounters can be challenging. Strategies to address this include training telehealth nurses in virtual communication skills, utilizing video conferencing for face-to-face interactions, and employing patient engagement tools within telehealth platforms [61].
- Workflow integration challenges for telehealth nursing: Integrating telehealth nursing workflows into existing hospital operations can be complex. Carefully planning telehealth workflow integration, streamlining processes, and providing clear roles and responsibilities for telehealth team members are crucial for successful implementation. Workflow optimization and process redesign are often necessary [57].
- Measuring the ROI of telehealth nursing programs: Demonstrating the return on investment (ROI) of telehealth nursing programs can be challenging. Developing robust metrics to capture the financial and clinical benefits of telehealth nursing, conducting cost-benefit analyses, and tracking long-term outcomes are essential to demonstrate program value and secure continued investment [56].
Conclusions
In conclusion, this comprehensive review has highlighted the transformative potential of telehealth nursing tools and strategies for optimal patient care doi within the framework of effective hospital administration. Telehealth nursing is not merely a technological add-on but a fundamental shift in healthcare delivery that requires strategic administrative leadership, financial investment, workforce development, and a commitment to quality and patient safety. Hospital administrators are pivotal in driving the successful integration of telehealth nursing, ensuring its ethical implementation, and leveraging its capabilities to enhance patient outcomes across the care continuum.
The future of hospital administration is inextricably linked to the advancement and effective utilization of telehealth nursing. Emerging technologies, evolving healthcare policies, and a growing emphasis on patient-centered and value-based care will further accelerate the adoption of telehealth nursing. To realize the full potential of telehealth nursing, healthcare leaders and policymakers must prioritize the development of telehealth-savvy administrators, invest in telehealth infrastructure and training, promote supportive regulatory frameworks, and address digital health equity. By embracing telehealth nursing as a core strategy, hospital administration can pave the way for a future of healthcare that is more accessible, efficient, patient-centered, and ultimately, leads to optimal patient outcomes for all.
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Author Contributions
Concept and design: Deepak Bhati, Meena S. Deogade, Deepika Kanyal
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: Deepak Bhati, Meena S. Deogade, Deepika Kanyal
Drafting of the manuscript: Deepak Bhati, Meena S. Deogade, Deepika Kanyal
Critical review of the manuscript for important intellectual content: Deepak Bhati, Meena S. Deogade, Deepika Kanyal
Supervision: Deepika Kanyal
References
[References from original article, ensure they are relevant and correctly formatted]
[1] …
[2] …
…
[62] …
(Note: Please replace “… ” with the actual references from the original article and ensure they are formatted correctly in markdown. Also, remember to verify the relevance of each reference to the new article’s focus on telehealth nursing.)