Early detection and treatment of mental health disorders are crucial for improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs. This comprehensive review examines various screening tools available for mental health assessment in primary care settings, focusing on their psychometric properties and applicability for primary care physicians (PCPs).
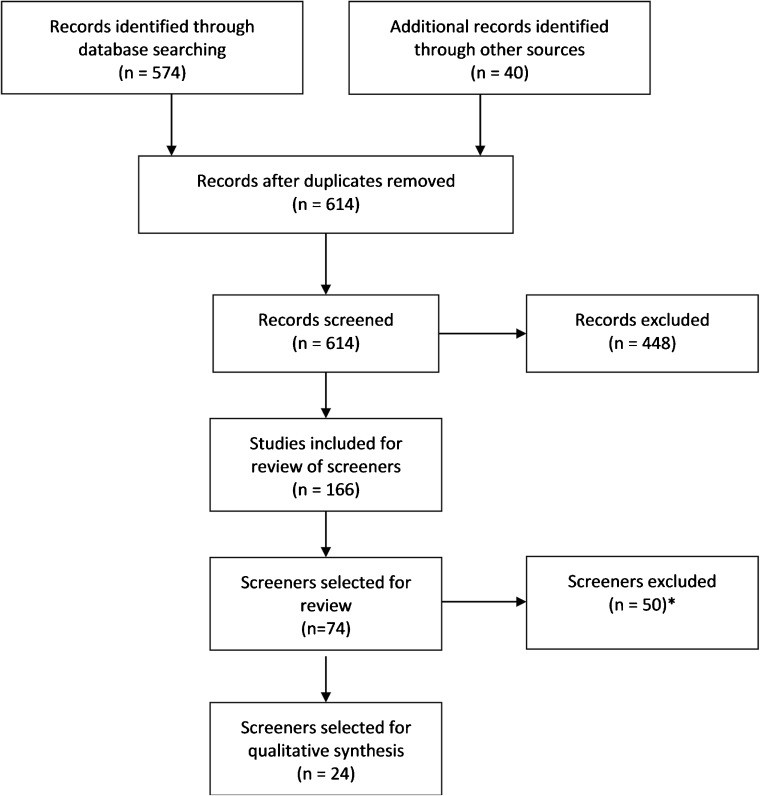 Flow chart for article selection
Flow chart for article selection
The rising prevalence of mental health disorders necessitates effective screening strategies in primary care. This allows for early intervention and improved patient care. This review aims to equip PCPs with the knowledge to choose and implement appropriate screening tools for common mental and substance use disorders in their practice.
Screening Tools for Multiple Conditions: PHQ and PSQ
The Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) and Patient Stress Questionnaire (PSQ) offer several validated subscales for screening various mental health and substance use disorders. These include:
- PHQ-9: A nine-item scale for detecting major depressive disorder, with excellent sensitivity and specificity.
- PHQ-15: A 15-item scale assessing somatization syndromes and symptoms.
- GAD-7: A seven-item scale for identifying generalized anxiety disorder.
- AUDIT-10: A ten-item tool for screening hazardous alcohol use.
These tools can be administered individually or combined for a comprehensive assessment. Shorter versions, such as the PHQ-2, GAD-2, PHQ-4, and AUDIT-C, offer briefer screening options with good psychometric properties.
Additional Multi-Disorder and Ultra-Short Tools
Beyond the PHQ and PSQ, several other tools exist for screening multiple mental or substance use disorders:
- HADS: The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale screens for both anxiety and depression.
- WB-DAT: The Web-Based Depression and Anxiety Test offers a computer-based assessment of various anxiety and depressive disorders.
- DAST-10: The Drug Abuse Screen Test identifies problems related to drug use (excluding alcohol and tobacco).
- ASSIST: The Alcohol, Smoking and Substance Involvement Screening Test assesses risk levels for various substances.
Ultra-short tools, typically with five or fewer items, offer rapid screening options for specific conditions:
- MHI-5: The Mental Health Inventory-5 provides a brief assessment of mental well-being.
- WHO-5: The World Health Organization-Five Well-Being Index screens for depressive disorders.
- CAGE: A four-item questionnaire specifically designed to screen for alcohol-related problems.
- Single-item screeners: Tools like the Single Question Screening Test for Drug Use and the Single Alcohol Screening Question provide extremely brief assessments.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Practice
Selecting the optimal screening tool depends on various factors, including:
- Patient population: Consider the prevalence of specific mental health conditions within your patient base.
- Clinic resources: Factor in available staff time, reimbursement policies, and access to behavioral health specialists for follow-up care.
- Psychometric properties: Evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of each tool, considering the potential for false positives and negatives.
PCPs should develop a clear protocol for managing patients who screen positive, ensuring appropriate follow-up care and referral to specialized services when necessary. Implementing effective screening protocols in primary care is paramount for early identification, treatment, and ultimately improved patient outcomes in mental health.

