Depression is a prevalent mental health disorder among adults, necessitating effective screening and treatment strategies in primary care settings. This article examines the implementation of VitalSign6, a measurement-based care (MBC) program, aimed at improving depression screening and treatment in a primary care setting at an academic medical center. We will discuss the effectiveness of this program in enhancing the identification and management of depression, along with its impact on screening rates, patient outcomes, and provider satisfaction.
The Importance of Depression Screening in Primary Care
Depression significantly impacts individual well-being and societal costs. Untreated depression can lead to emotional suffering, reduced productivity, strained relationships, and increased risk of comorbid conditions. Recognizing the crucial link between mental and physical health, evidence highlights the frequent coexistence of depression with chronic diseases. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends screening all adults for depression in primary care, employing evidence-based protocols to ensure effective identification and intervention.
Utilizing Evidence-Based Screening Tools: PHQ-2 and PHQ-9
The Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ)-2 and PHQ-9 are widely recognized and validated Screening Tools For Depression In Primary Care. The PHQ-2, a concise two-question tool assessing depressed mood and anhedonia, serves as an initial screening step. A PHQ-2 score of 3 or higher warrants further evaluation with the more comprehensive PHQ-9. The PHQ-9, a nine-item questionnaire aligned with DSM-5 criteria for major depressive disorder, provides a more detailed assessment of symptom severity. These tools, when combined with comprehensive systems of care, including standardized protocols and referral systems, contribute to improved long-term outcomes and remission rates for individuals with depression.
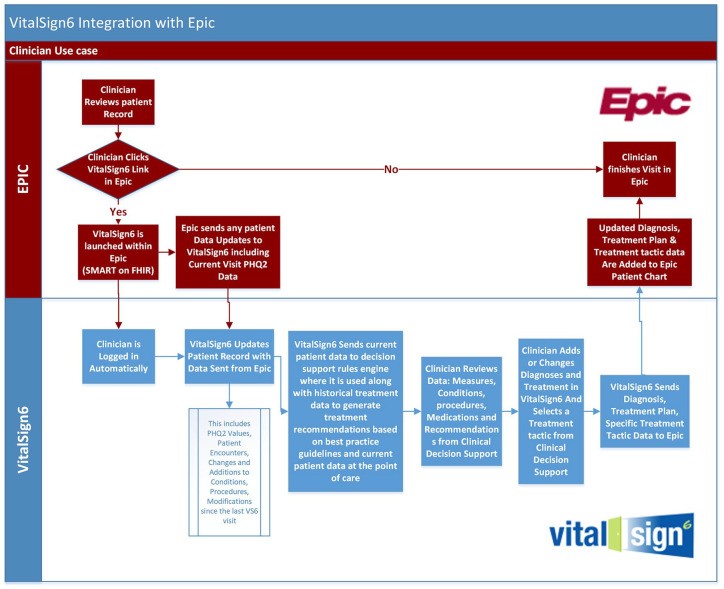
Implementing VitalSign6: A Measurement-Based Care Approach
VitalSign6, a web-based MBC program, offers primary care providers a comprehensive suite of tools for depression management. Utilizing validated questionnaires, symptom tracking, and clinical decision support (CDS), VitalSign6 facilitates diagnosis, treatment planning, and ongoing monitoring. The program’s integration with electronic health records (EHRs) streamlines workflow and enables real-time access to patient data and treatment recommendations. By leveraging technology and evidence-based practices, VitalSign6 empowers primary care providers to deliver personalized and effective depression care.
Evaluating the Impact of VitalSign6
A pre-post intervention study assessed the effectiveness of VitalSign6 implementation. Results demonstrated a significant increase in depression screening rates, exceeding the target of 75%. Of the patients screened, a substantial proportion were diagnosed with depression and received MBC-guided treatment. Furthermore, patients participating in follow-up care exhibited a statistically significant decrease in self-reported PHQ-9 scores, indicating a positive impact on depression symptoms.
Provider and Staff Satisfaction with VitalSign6
While VitalSign6 demonstrated positive impacts on screening and patient outcomes, provider and staff feedback revealed challenges related to workflow integration and technical issues. Some providers reported that the program slowed down clinic workflow, while others experienced difficulties with EHR interoperability. Despite these challenges, both physicians and staff acknowledged the value of VitalSign6 in raising mental health awareness and improving depression screening practices.
Conclusion: VitalSign6 as an Adjunct to Depression Care
VitalSign6 shows promise as a valuable tool for enhancing the identification and management of depression in primary care. The program’s strengths lie in its comprehensive approach to MBC, EHR integration, and utilization of validated screening tools. However, addressing workflow and interoperability challenges is crucial for optimizing its implementation and ensuring long-term sustainability. Future research should focus on refining workflow processes, improving EHR integration, and exploring strategies to enhance patient retention in follow-up care. By addressing these challenges, VitalSign6 can play a pivotal role in improving the lives of individuals affected by depression.