In the evolving landscape of healthcare, home health agencies (HHAs) are playing an increasingly vital role in delivering care directly to patients’ homes. This shift emphasizes the need for robust systems that not only ensure the quality of care but also continuously improve it. Quality Assurance and Performance Improvement (QAPI) programs are emerging as indispensable frameworks for HHAs aiming to elevate their standards, enhance patient safety, and streamline operations. These data-driven and proactive approaches are more than just regulatory checkboxes; they represent a commitment to excellence in the comfort of patients’ residences.
This article explores how QAPI serves as a crucial tool for home health agencies to tackle challenges and boost the quality of care they provide, ensuring that patients receive the best possible support in their home environment.
What is QAPI for Home Health Agencies?
QAPI, standing for Quality Assurance and Performance Improvement, is a systematic, data-led, and forward-thinking methodology designed to enhance the quality of healthcare services across various settings, including home health agencies. For HHAs, QAPI is particularly critical as it provides a structured approach to consistently raise the bar of care delivered to patients within their homes, especially under the Medicare Part A benefit. This encompasses medically necessary skilled care provided intermittently, such as nursing, physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech-language therapy, all prescribed by a physician.
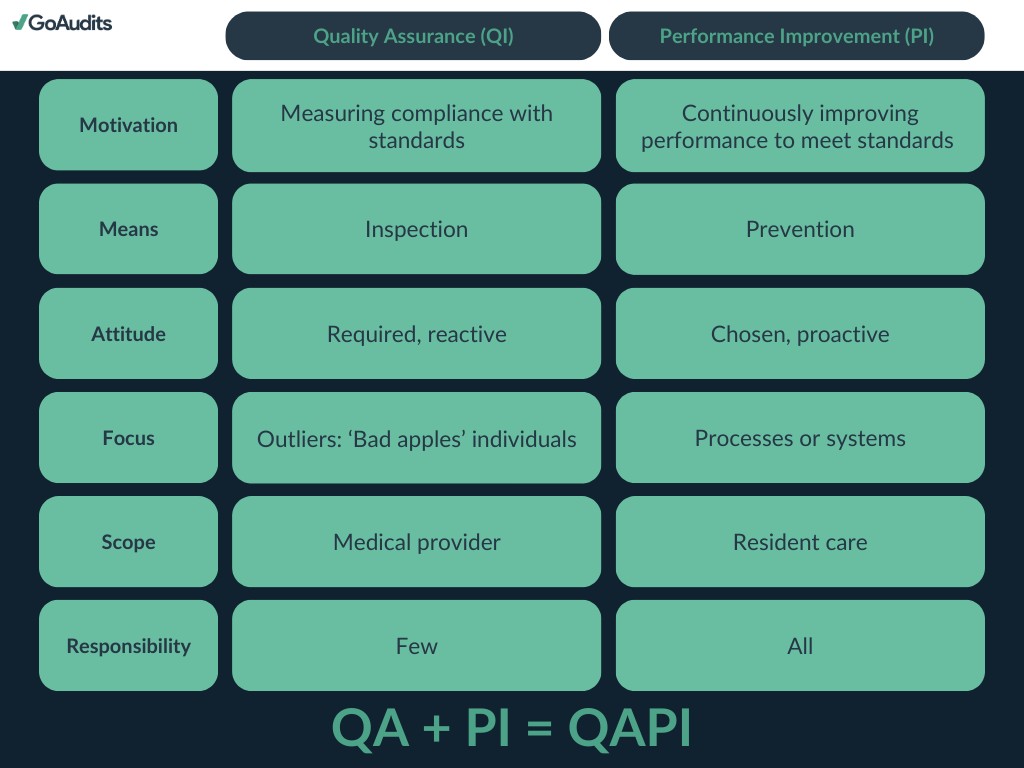
The QAPI framework in home health care operates on two core pillars:
- Quality Assurance (QA): This aspect involves the methodical gathering and assessment of data to monitor the results of care processes. QA aims to confirm that the care provided adheres to established standards and regulations. By identifying areas where care quality may fall short, QA activities ensure compliance with both federal and state mandates.
- Performance Improvement (PI): PI is dedicated to the systematic enhancement of agency processes and systems to improve patient care quality and outcomes. This involves pinpointing areas for improvement, implementing strategic changes, and measuring the effectiveness of these changes to ensure lasting improvements.
QAPI programs necessitate a comprehensive quality enhancement strategy within home health agencies, engaging all organizational levels from leadership to frontline staff. Agencies are expected to set clear, measurable goals and utilize data to inform their decision-making processes. This includes analyzing a range of metrics such as patient outcomes, satisfaction levels, and operational efficiency.
💡 In 2021, the United States was home to 11,474 Medicare-certified HHAs, serving approximately 3 million Medicare Fee for Service (FFS) beneficiaries. In the preceding year, 2020, 8.3% of all Medicare FFS beneficiaries availed themselves of home health care services.
Given the substantial number of Medicare-certified HHAs and the millions of beneficiaries relying on home health care across the nation, effective QAPI programs are indispensable for upholding high care standards, ensuring patient safety, and driving positive patient outcomes nationwide.
Implementing QAPI in Home Health Settings
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) strongly emphasizes QAPI as part of its broader initiative to enhance healthcare results and patient contentment, while also aiming to reduce costs within home health agencies.
A cornerstone of CMS’s strategy to incentivize quality improvement in home health care is the Home Health Value-Based Purchasing (HHVBP) model. This model adjusts payments to home health agencies based on the quality of care they deliver, incentivizing them to improve both the quality and efficiency of their services, with a primary focus on achieving better health outcomes for patients.
Within the HHVBP model, QAPI is not just beneficial—it’s essential. Home health agencies are mandated to have QAPI programs in place as stipulated by the Home Health Conditions of Participation (CoPs). HHAs are expected to apply QAPI principles to identify areas needing improvement and to implement strategies that elevate care quality. Agency performance under the HHVBP model is evaluated using a set of quality measures reflecting care outcomes and processes, patient experience, and other pertinent indicators.
Key QAPI resources for home health agencies include:
- CoP Final Home Health Agency Interpretive Guidance, Effective August 2018
- CoP for Home Health Agencies, Effective January 2018
- Data-driven QAPI program for home health agencies (§484.65)
Key Elements of a Home Health QAPI Program
CMS outlines the requirements for QAPI programs across five essential categories, often referred to as the five QAPI elements or standards.
💡 Delve deeper into the 5 elements of QAPI in healthcare to understand their broader application.
These elements are designed to guide HHAs in developing, implementing, and sustaining QAPI programs that not only meet CMS requirements but also drive meaningful performance improvements.
- Design and scope
- Governance and leadership
- Feedback, data systems, and monitoring
- Performance improvement projects (PIPs)
- Systematic analysis and action
1. Program Scope
- 484.65(a)(1): A QAPI program must be structured to demonstrate quantifiable improvements in indicators linked to better health outcomes, enhanced patient safety, and superior care quality. This necessitates focusing the program on areas where improvements are most likely to yield significant positive impacts on patient outcomes.
- 484.65(a)(2): HHAs are required to measure, analyze, and consistently track quality indicators, including any adverse patient events. This involves a thorough assessment of care processes, services provided, and overall agency operations to ensure they meet the desired benchmarks for quality and safety.
2. Program Data
- 484.65(b)(1): The utilization of quality indicator data is paramount. This includes data sourced from the Outcome and Assessment Information Set (OASIS) and other relevant sources to inform the QAPI program’s design and direction.
- 484.65(b)(2): Data collection must be employed to monitor service safety and quality, identify opportunities for enhancement, evaluate the effectiveness of implemented changes, and confirm that care is consistently delivered in a safe manner.
- 484.65(b)(3): The frequency and level of detail in data collection must be approved by the HHA’s governing body, ensuring that data-driven insights effectively support the QAPI program’s objectives and activities.
3. Program Activities
- 484.65(c)(1): Performance improvement activities should be strategically directed towards areas identified as high risk, high volume, or prone to problems. The focus should be on the severity and prevalence of issues to facilitate prompt correction of any problems that pose a threat to patient health and safety. Solutions like GoAudits’ incident reporting feature can provide immediate tracking and causal analysis of adverse patient events.
- 484.65(c)(2): These activities must include a systematic approach to tracking adverse patient events, thoroughly analyzing their root causes, and implementing proactive measures to prevent future occurrences.
- 484.65(c)(3): Following the implementation of improvement actions, HHAs are required to measure the success of these actions and continuously monitor performance to ensure that improvements are not only achieved but also sustained over time.
4. Performance Improvement Projects
- 484.65(d)(1): HHAs are obligated to undertake a defined number of performance improvement projects annually. The scope and complexity of these projects should reflect the range and nature of the agency’s services and operational history.
- 484.65(d)(2): Comprehensive documentation of each project is essential. This documentation should include the rationale behind the project, the methodologies employed, the progress achieved, and the outcomes, demonstrating a clear commitment to ongoing improvement.
5. Executive Responsibilities
- 484.65(e): The governing body of the HHA bears ultimate responsibility for the QAPI program. This encompasses ensuring the program is well-defined, effectively implemented, and actively maintained. It also includes setting priorities for quality and patient safety, establishing clear expectations for patient safety protocols, and decisively addressing any findings related to fraud or waste.
💡 Discover how these 5 QAPI elements form the foundational framework for any effective QAPI plan across various healthcare environments, including nursing homes and hospices.
Addressing Challenges in Home Health Care with QAPI
Home health agencies encounter unique challenges in maintaining and enhancing care quality, distinct from those faced by other healthcare providers.
- Staff Recruitment and Retention
A persistent challenge in the home health industry is attracting and keeping qualified staff. This includes not only skilled nurses and therapists but also home health aides, who are vital for daily patient care. High staff turnover particularly complicates quality processes and regulatory compliance. Addressing this requires focusing on factors like comprehensive training programs, competitive compensation and benefits, and fostering job satisfaction.
- Quality of Care and Patient Safety
Maintaining superior care standards and ensuring patient safety are of utmost importance. This involves creating thorough training programs, integrating technology for enhanced care management, and actively participating in quality improvement initiatives. The individualized nature of home health care necessitates a strong emphasis on culturally sensitive care and addressing each patient’s unique needs.
- Patient Engagement and Education
Actively involving patients and their families in care planning is crucial for achieving positive home health outcomes. Educating them about managing their conditions, adhering to medication schedules, and preventive health measures can significantly improve health outcomes and decrease hospital readmission rates.
- Coordination with Other Healthcare Providers
Effective communication and seamless coordination with a broader network of healthcare providers, including primary care physicians, specialists, and hospitals, are essential for ensuring continuity of care. This demands efficient information exchange and robust collaboration across different care settings.
- Regulatory Compliance and Reimbursement
Home health agencies operate within a complex web of regulations and compliance requirements. Changes in healthcare legislation, Medicare, and Medicaid policies can significantly impact service delivery models and reimbursement structures.
Leveraging Technology: GoAudits as a QAPI Tool
GoAudits’ healthcare auditing app provides HHAs with a powerful tool to conduct diverse checks and audits, covering patient care, safety protocols, and adherence to care standards. GoAudits simplifies the process of collecting data and documentation necessary for QAPI programs, offering a mobile-friendly auditing solution that functions both online and offline.
Featuring real-time reporting, customizable checklists, and secure centralized data storage, GoAudits delivers essential functionalities that empower HHAs to uphold high care standards and improve overall operational effectiveness as part of their QAPI initiatives.
Benefits of QAPI Implementation for Home Health Agencies
Implementing QAPI programs offers numerous advantages for home health agencies:
- Improved Patient Care: By focusing on identifying and resolving issues within care processes, QAPI leads to enhanced patient outcomes and greater patient satisfaction.
- Reduced Costs: QAPI programs help agencies identify and eliminate inefficiencies and waste, leading to cost reductions and improved financial health.
- Increased Regulatory Compliance: QAPI assists agencies in meeting all relevant regulations, thereby minimizing the risk of penalties and fines.
- Potential for Increased Reimbursement: Effective QAPI programs can qualify HHAs for incentives and rewards from payers like Medicare.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: QAPI’s reliance on data collection and analysis enables agencies to make informed decisions based on concrete evidence and outcomes.
- Enhanced Risk Management: QAPI programs aid in identifying and mitigating potential risks, reducing the likelihood of adverse events and enhancing patient safety.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration: QAPI promotes better communication and teamwork across departments and among team members, fostering a unified, patient-focused approach to care.