The OBD2 port, a standard feature in modern vehicles, allows access to a wealth of diagnostic information. Among its various communication protocols, the K-line, part of the ISO 9141-2 standard, plays a crucial role. This article delves into understanding OBD2 K-line voltage, its significance in vehicle diagnostics, and its role within the broader context of OBD2 communication.
 OBD-II connector and pinouts
OBD-II connector and pinouts
The On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) system, mandated in vehicles since 1996, revolutionized vehicle diagnostics. This system, known as OBD-II, utilizes a standardized 16-pin connector, often called the DLC (Data Link Connector), located under the dashboard. Through this port, a scan tool can access Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), providing insights into vehicle malfunctions. Beyond diagnostics, the OBD2 port supports functionalities like vehicle tracking, leveraging GPS technology to monitor location and speed. This constant power supply to the OBD2 port, even when the vehicle is off, makes it susceptible to electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage. Protecting the circuitry with Transient Voltage Suppression (TVS) diodes is critical to prevent damage to both the vehicle and connected devices.
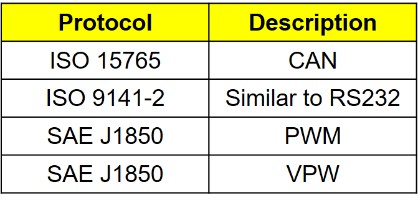
The OBD2 port supports various communication protocols, including ISO 15765 (CAN), SAE J1850 (PWM and VPW), and ISO 9141-2 (K-Line and L-Line). Each protocol uses different pins and signal characteristics. The ISO 9141-2 protocol, utilizing the K-line for primary communication and the L-line for initialization, operates with a maximum data rate of 10.4Kbps and a signal voltage up to 12V. The OBD2 K-line voltage, typically around 12V, represents the signal level on pin 7 of the OBD2 connector. This voltage fluctuates as data is transmitted, allowing communication between the vehicle’s ECU and diagnostic equipment. Understanding the specific voltage levels and their variations is crucial for accurate data interpretation and diagnostics.
The K-line’s significance lies in its ability to facilitate bi-directional communication between the scan tool and the vehicle’s control modules. It allows for requesting diagnostic data, performing actuator tests, and even reprogramming certain modules. While newer vehicles predominantly use CAN bus communication, the K-line remains prevalent in older models, making it a vital component for comprehensive vehicle diagnostics.
In conclusion, understanding OBD2 K-line voltage is essential for anyone working with vehicle diagnostics. Its role in the ISO 9141-2 protocol, its typical voltage range, and its function in facilitating communication make it a fundamental aspect of OBD2 technology. This knowledge is crucial for accurate troubleshooting, data interpretation, and effective utilization of diagnostic equipment. As vehicle technology continues to evolve, understanding the foundational principles of communication protocols like the K-line remains vital for comprehensive diagnostics and repair.
