OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics) codes are essential for diagnosing car problems. These codes, retrieved using an OBD2 scanner, provide valuable insights into the health of your vehicle’s systems. Innova, a leading provider of diagnostic tools, offers comprehensive resources for understanding these codes. This article delves into the structure and meaning of Innova Obd2 Codes, empowering you to troubleshoot automotive issues effectively.
Decoding Innova OBD2 Codes
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), often referred to as Innova OBD2 codes when using an Innova scanner, pinpoint malfunctions within your vehicle’s systems. These alphanumeric codes guide mechanics and car owners toward the root cause of automotive problems, enabling efficient repairs. Consulting your vehicle’s service manual in conjunction with the DTC is crucial for accurate diagnosis and repair. Don’t rely solely on codes; always verify findings with proper testing procedures outlined in the service manual.
 Diagnostic Trouble Codes image 1.png__PID:51e055f6-3586-4dc5-b14e-749efd4b0166
Diagnostic Trouble Codes image 1.png__PID:51e055f6-3586-4dc5-b14e-749efd4b0166
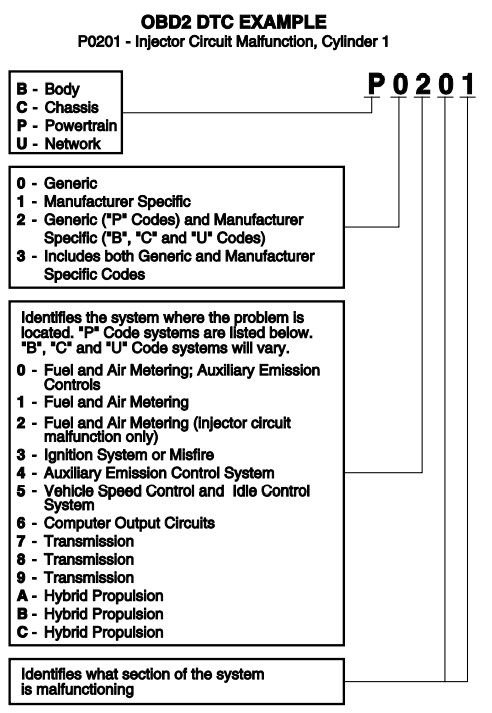
Each Innova OBD2 code consists of five characters:
The First Character: System Identification
The initial letter signifies the main system where the fault originated:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission, emissions)
- B: Body (air conditioning, power seats, airbags)
- C: Chassis (ABS, suspension, steering)
- U: Network (communication systems)
The Second Character: Code Type
The second character, a number from 0 to 3, indicates whether the code is generic or manufacturer-specific:
- 0: Generic (SAE – Society of Automotive Engineers) – Standardized across all vehicle manufacturers.
- 1-3: Manufacturer-Specific – Unique to the vehicle’s make. Innova’s database often provides detailed descriptions for these codes. While generic codes cover common issues, manufacturer-specific codes offer more granular diagnostics for complex systems.
The Third Character: Subsystem Identification
This character, a letter or number, pinpoints the specific subsystem affected (e.g., fuel system, ignition system).
The Fourth and Fifth Characters: Fault Location
These two characters further narrow down the problem area within the subsystem, indicating the specific component or circuit malfunctioning.
Utilizing Innova’s DTC Library
Innova provides a comprehensive DTC library (https://www.innova.com/pages/dtc-library) containing detailed descriptions of both generic and manufacturer-specific codes. This invaluable resource helps decipher complex codes, streamlining the diagnostic process. By leveraging Innova’s resources and understanding the structure of OBD2 codes, you gain a significant advantage in troubleshooting car problems.
Conclusion
Innova OBD2 codes are indispensable tools for automotive diagnostics. Understanding their structure and utilizing resources like Innova’s DTC library empowers you to effectively address car issues. Remember, while OBD2 codes are vital, always consult your vehicle’s service manual for comprehensive testing procedures and accurate repairs. By combining code information with proper diagnostic techniques, you can confidently maintain and repair your vehicle.

