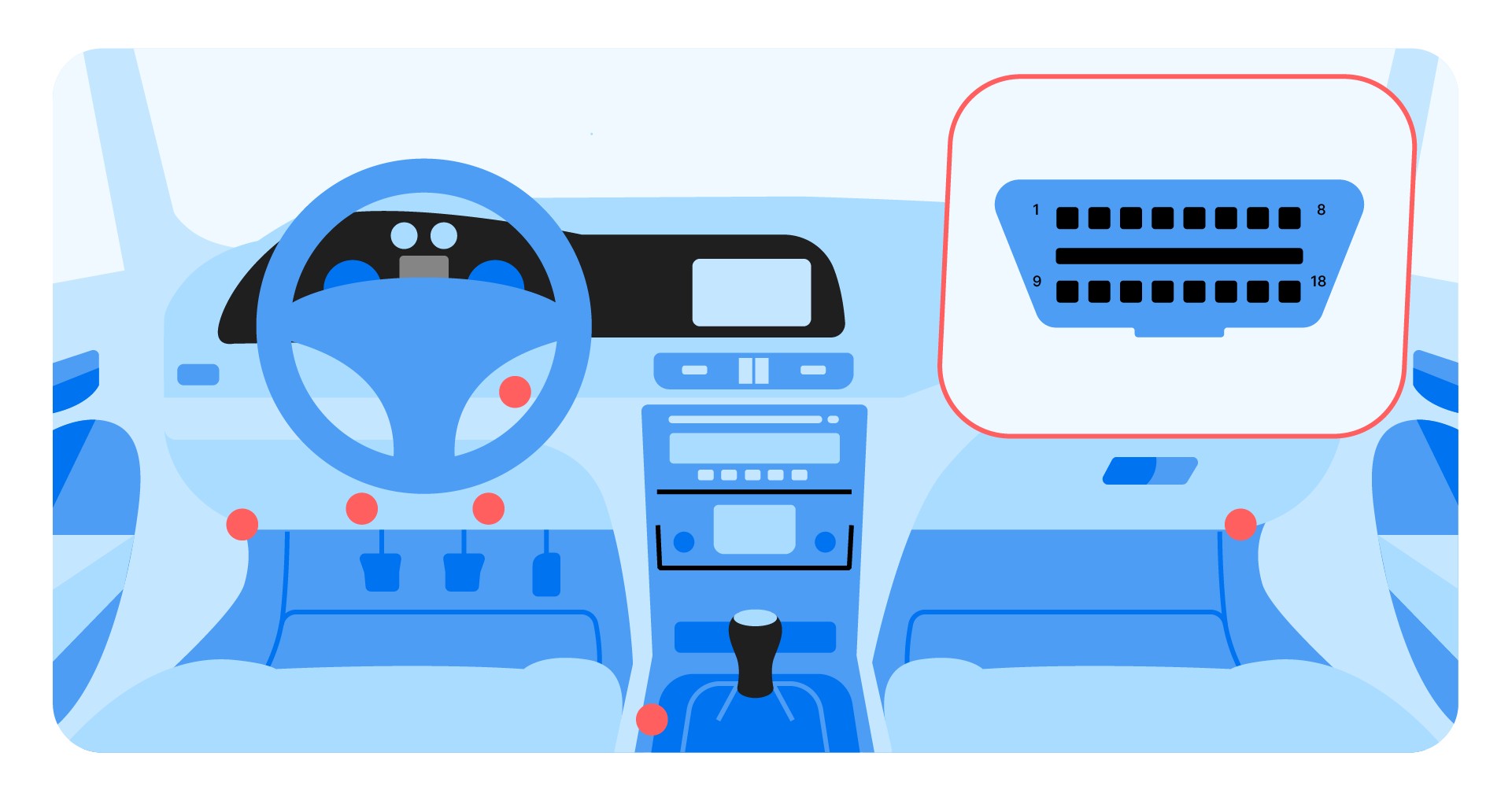
Connecting an OBD2 scanner to your car can feel like unlocking a secret language. This guide will walk you through how to use an OBD2 scanner, demystifying fault codes and live data to help you understand your vehicle’s health.
Source: carVertical
Understanding the OBD2 Scanner
An OBD2 (On-Board Diagnostics) scanner is a diagnostic tool that connects to your car’s OBD2 port, typically located under the steering wheel. It retrieves information from the car’s computer, providing valuable insights into potential issues. This information includes:
- Fault Codes: These codes indicate specific problems within the vehicle’s systems.
- Live Data: Real-time readings from various sensors, such as engine speed, temperature, and pressure.
Source: Flickr / shixart1985
Types of OBD2 Scanners
Several types of OBD2 scanners cater to different needs:
- Basic Code Readers: These affordable Bluetooth devices pair with your smartphone to read fault codes and some live data. Ideal for the average driver.
- DIY Scanners: More advanced scanners with features like resetting service reminders and activating service functions. Suitable for those tackling minor repairs.
- Professional Scanners: High-end tools with extensive coding and programming capabilities used by mechanics and automotive professionals.
Using an OBD2 Scanner: A Step-by-Step Guide
Here’s how to use an OBD2 scanner effectively:
1. Locate and Connect the Scanner
Find the OBD2 port in your car (usually under the dashboard) and plug in the scanner. For Bluetooth scanners, ensure pairing with your device.
2. Turn on the Ignition
Turn the ignition key to the “on” position (without starting the engine). This powers up the car’s computer system, allowing the scanner to communicate. Turn off accessories like the radio and AC to minimize power consumption.
3. Select Vehicle Information
Some scanners require you to manually input your car’s make, model, and year. Others automatically detect this information via the VIN.
4. Initiate the Scan
Select the “scan” or “read codes” option on the scanner. Choose between a full system scan or scanning specific modules.
Source: Flickr / comedy_nose
5. Interpret the Fault Codes
The scanner will display fault codes, such as “P0171” or “U0100.” Refer to a reliable OBD2 code database or repair manual to understand the meaning of each code.
6. Analyze Live Data (Optional)
Advanced scanners allow you to monitor live data streams. This helps pinpoint issues by observing sensor readings in real-time. For example, you might monitor fuel pressure or engine RPM while driving.
Clearing Fault Codes
After addressing the underlying issue, you can use the scanner to clear the fault codes. However, simply clearing codes without fixing the problem is not recommended.
OBD2 Scanners and Used Car Purchases
An OBD2 scanner can be invaluable when buying a used car. It helps uncover hidden problems that might not be apparent during a test drive. Always scan a used car before buying to avoid potential headaches.
Conclusion
Learning how to use an OBD2 scanner empowers you to understand your car’s health, diagnose potential problems, and make informed repair decisions. While not a replacement for professional mechanics, it’s a valuable tool for any car owner. A thorough vehicle inspection, coupled with a vehicle history report, is crucial for informed decision-making.