The 4R44E transmission, along with its siblings the 4R55E, 5R44E, and 5R55E, can sometimes throw the dreaded flashing overdrive (OD) light. This indicates an issue detected by the onboard diagnostics (OBD2) system, often resulting in diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) such as P0743 (Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Electrical) and P0760 (Shift Solenoid C Malfunction). This guide focuses on performing an OBD2 test to diagnose these common 4R44E transmission problems.
Understanding these codes and how to test related components is crucial for effective troubleshooting. The P0743 code suggests an electrical problem within the torque converter clutch (TCC) circuit, while the P0760 code points to a malfunction in shift solenoid C, which controls overdrive.
 4r44e transmission connector
4r44e transmission connector
Electrical Checks: The Foundation of 4R44E Diagnostics
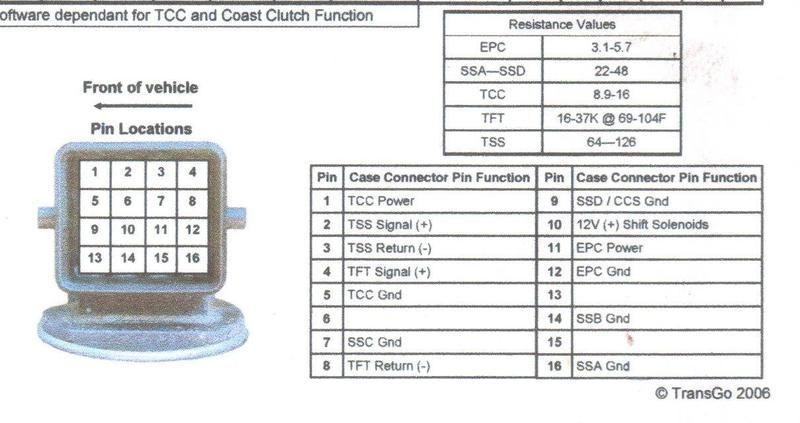
Before delving into specific component tests, it’s essential to verify the integrity of the transmission’s electrical system. The 4R44E uses a 16-pin connector located on the driver’s side of the transmission. This connector provides power and ground to the solenoids and allows the transmission control module (TCM) to monitor their operation.
Begin by disconnecting the 16-pin connector. With the key on and engine off (KOEO), you should have 12 volts present at pins 1, 10, and 11. These pins supply power to the various solenoids. A simple test with a multimeter can confirm this. If voltage is absent, check for blown fuses or a faulty power source.
Next, inspect the wiring harness for damage, loose connections, or corrosion. Any issues found here should be addressed before proceeding. A damaged harness can cause intermittent problems that are difficult to diagnose. Even a slightly loose connection can interrupt the signal and trigger a fault code.
Testing Solenoids and Wiring with an Ohmmeter
With the connector still disconnected, you can test the resistance of the solenoids and their associated wiring. Using an ohmmeter, perform the following tests:
- Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Solenoid: Measure the resistance between pin 1 and pin 5. A reading between 9 and 16 ohms indicates a healthy TCC solenoid.
- Pressure Control Solenoid: Test the resistance between pin 11 and pin 12. The expected range is 3 to 6 ohms.
- Shift Solenoids (SSA-SSD): Measure the resistance between pin 10 and each of the four shift solenoid pins. You should observe a reading between 22 and 48 ohms for each solenoid.
These resistance checks help identify open circuits, shorts, or faulty solenoids. Any readings outside the specified ranges warrant further investigation. A low resistance reading could indicate a short circuit, while a high or infinite reading suggests an open circuit.
Understanding Transmission Operation and Diagnostic Codes
The TCM relies on various inputs to control shifting and torque converter lockup. It monitors engine speed, input shaft speed (via the Turbine Speed Sensor or TSS), and the status of the solenoids.
When the TCC solenoid is energized, the torque converter should lock, causing the engine and input shaft speeds to synchronize. If the engine speed increases but the input shaft speed doesn’t match, the torque converter isn’t locking properly. However, the P0743 code suggests an electrical fault rather than a performance issue.
Similarly, when shifting into overdrive, the engine speed should drop. If it doesn’t, the overdrive isn’t engaging correctly. The P0760 code indicates a problem with the overdrive solenoid (Solenoid C). While band adjustments can sometimes affect overdrive operation, the P0760 code points directly to an electrical issue with the solenoid itself.
Conclusion: Next Steps in 4R44E Diagnosis
Successfully troubleshooting 4R44E transmission problems requires a systematic approach. Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the wiring harness and connector. Then, perform the key electrical tests outlined above to pinpoint the source of the issue. Remember, while this guide focuses on electrical diagnostics related to P0743 and P0760, mechanical problems can also contribute to transmission malfunctions. If the electrical checks don’t reveal the problem, further diagnosis may be necessary, potentially involving a professional scan tool and more advanced testing procedures. A complete understanding of transmission operation and the information provided by the OBD2 system is essential for accurate diagnosis and repair.
