The landscape of health care is undergoing a seismic shift, fueled by the rapid advancement and integration of artificial intelligence (AI). The sheer volume of AI-powered health tools available is staggering, mirroring the immense potential they hold. Currently, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has given its stamp of approval to nearly 900 AI health tools. Experts are increasingly advocating for their adoption to bolster patient care, particularly as the healthcare system grapples with persistent physician shortages and concerning hospital closures. These challenges underscore the urgent need for innovative solutions, and Ai Tools For Health Care are emerging as a critical part of the answer.
However, the sheer availability of FDA-approved AI tools doesn’t automatically translate to tangible benefits. As Nigam Shah, PhD, a leading data scientist at Stanford Health Care, points out, the crucial question is whether these tools genuinely enhance patient care while simultaneously driving down costs. “Are we going to make things better or worse?” Shah questions, emphasizing the current lack of comprehensive regulation in this rapidly evolving field. His team at Stanford has proactively developed AI assessment processes specifically for healthcare systems to navigate this complex terrain.
To help healthcare professionals effectively navigate the vast ocean of AI options, we consulted with Shah and other industry experts to identify the AI tools that are currently making the most significant impact in hospitals and clinics. Our curated list prioritizes commercially available tools that have garnered attention from multiple experts and/or have received recognition from organizations dedicated to standardizing AI assessment, such as the Coalition for Health AI and the Health AI Partnership.
The following represents our top five AI tools for health care available today – a list of solutions that are currently leading the charge in transforming medical practice, until the next wave of innovation inevitably arrives.
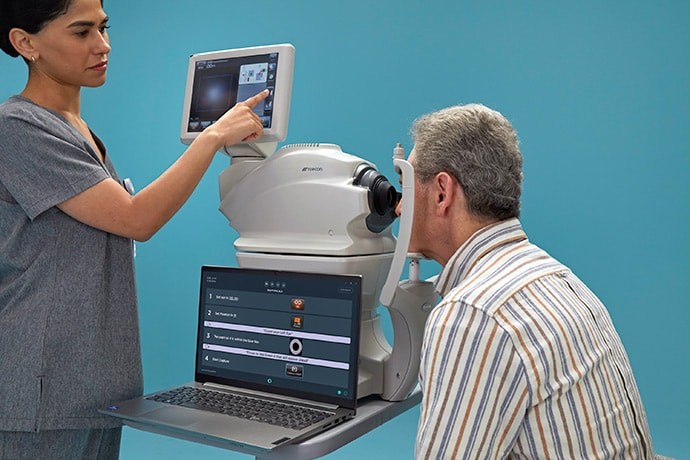
1. LumineticsCore: AI-Powered Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis at the Point of Care
What it is: An AI-driven diagnostic system for diabetic retinopathy.
Who it’s for: Optometrists, ophthalmologists, primary care physicians, and endocrinology clinics – point-of-care providers across various specialties.
Diabetic retinopathy, a serious eye condition affecting nearly half of individuals with diabetes, is the primary cause of blindness in the United States. Alarmingly, it’s estimated that approximately half of those affected are unaware they have the condition. Early detection through eye exams is critical, but traditional diagnostic processes can involve delays of a week or more for results, often leading to patient drop-off in follow-up care.
LumineticsCore, an FDA-approved AI tool, is revolutionizing the diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy and macular edema by significantly accelerating the process. This AI tool for health care is designed for use at the point of care, meaning during the patient’s initial visit.
The system works by analyzing retinal images captured by a standard retinal camera. It employs a sophisticated AI-based algorithm coupled with a separate diagnostic algorithm to identify and analyze key biomarkers. This advanced analysis allows LumineticsCore to deliver a diagnosis during the same appointment, enabling immediate referrals to ophthalmologists for patients who need further care.
Research from Stanford researchers indicates that patients diagnosed using LumineticsCore are three times more likely to adhere to ophthalmologist referrals compared to those diagnosed through traditional clinical methods. Furthermore, LumineticsCore has successfully passed Stanford’s rigorous AI assessment, demonstrating a “clear increase in the quality of care,” according to Shah.
Jennifer Goldsack, founder and CEO of DiMe, a leading non-profit digital medicine organization, emphasizes another impactful aspect of LumineticsCore: the company assumes full liability for diagnostic accuracy. This crucial feature protects providers from liability in cases of misdiagnosis. Adding to its practical advantages, LumineticsCore also has a dedicated billing code, facilitating reimbursement from private insurance providers.
2. Abridge: AI-Powered Ambient Listening for Streamlined Clinical Documentation
What it is: An AI-driven ambient listening tool designed to automate clinical note-taking.
Who it’s for: Physicians across all specialties seeking to reduce administrative burden and computer time.
Bruce Darrow, PhD, interim chief digital and information officer at Mount Sinai Health System, envisions a “hospital of the future” where keyboards and manual typing are relics of the past. In this future, doctors and nurses communicate naturally, and AI seamlessly captures and routes the information where it’s needed. AI tools for health care like Abridge are bringing this vision closer to reality.
Abridge, originating from the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC), is an AI-powered ambient listening tool that exemplifies this future. Christian Carmody, MBA/MIS, chief technology officer at UPMC, highlights the efficiency gains: “This helps them [physicians] do that more efficiently, so they can spend more time taking care of patients,” referring to the often time-consuming task of documentation completion after patient encounters.
According to Abridge’s calculator, a hospital system with 200 physicians could potentially save approximately 85,000 hours annually – or 425 hours per physician – and reduce physician turnover costs (related to burnout) by $1.7 million per year by implementing Abridge.
Carmody notes the overwhelmingly positive feedback from physicians: “Almost universally, doctors have told us it frees up time every day that had been spent catching up on administrative notes.”
With patient consent, Abridge records patient-physician interactions and generates a real-time transcript. Its sophisticated AI algorithm then extracts crucial information to draft clinical notes, which clinicians review and finalize before adding to the patient’s electronic health record (EHR).
A unique feature of Abridge is its “explainable AI.” Users can highlight sections of the AI-generated note to instantly see the corresponding source in the transcript, ensuring verifiability and transparency. Abridge also extends access to recordings and transcripts to patients, promoting patient engagement and understanding.
Abridge is designed for seamless integration with Epic and other electronic health record systems. It is currently deployed at leading healthcare institutions including Emory Healthcare, Yale New Haven Health, Sutter Health, Christus Health, and The University of Chicago, demonstrating its growing adoption and impact.
3. Woebot: AI-Powered Mental Health Support Chatbot for On-Demand Assistance
What it is: A mental health chatbot leveraging machine learning to provide cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) based support.
Who it’s for: Primary care physicians and mental health specialists seeking to expand access to mental health resources.
The demand for mental health services is straining the healthcare system, with providers struggling to meet patient needs. Tarun Kapoor, MD, chief digital transformation officer at Virtua Health, points out the lengthy wait times – often weeks or months – that patients face to see a mental health specialist after referral requests. AI tools for health care are stepping in to bridge this gap.
Woebot is a mental health chatbot designed to provide on-demand support via a smartphone app. This AI tool employs principles of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and is accessible exclusively to patients of partner healthcare institutions, typically those with 50+ primary care physicians, according to Brad Gescheider, chief commercial officer at Woebot Health. While Woebot itself is not FDA-approved, a prior version (not currently available) received the FDA’s breakthrough device designation, a status that can expedite but doesn’t guarantee future approval.
Woebot utilizes machine learning to interpret patient messages and delivers pre-written responses crafted by the company’s team of clinicians and writers. These responses closely mirror the communication style of human clinicians, ensuring a therapeutic and empathetic interaction. The company intentionally avoids generative AI for chatbot responses in mental health contexts, citing concerns about unpredictability and the need for consistent, clinically sound interactions.
Virtua Health currently prescribes Woebot to a select group of patients experiencing mild to moderate depression and anxiety – conditions for which CBT has proven effective. Woebot is offered free of charge to Virtua Health patients, while hospitals and health systems pay a recurring monthly fee based on their number of primary care physicians.
Woebot, a two-time MedTech Breakthrough award recipient, is gaining popularity and demonstrating convenience. User engagement metrics are strong, with over 80% of users reporting satisfaction, typical interactions lasting just 7 minutes, and 77% of interactions occurring outside of traditional provider working hours. Impressed by these findings, one insurer has requested further data, signaling potential movement towards insurance reimbursement for this type of AI-driven mental health support.
Kapoor emphasizes the importance of demonstrating both utilization and patient benefit: “We have to show that people are using and getting benefit from the tools we’re recommending and we’re not just adding cost to the system.”
4. VBrain: AI-Assisted Brain Tumor Auto-Contouring for Radiation Oncology
What it is: An AI-powered tool for automated brain tumor contouring in radiation therapy planning.
Who it’s for: Radiation oncologists aiming to improve efficiency and accuracy in tumor delineation.
Accurate tumor contouring – the precise delineation of tumor location and mass – is a critical step in radiation oncology treatment planning. Identifying the exact “anatomical part” of each tumor is essential for radiation oncologists to deliver radiation effectively while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue, explains Shah. However, manual tumor contouring is an extremely labor-intensive and time-consuming process.
“[W]e’re putting dots and connecting them into an area,” Shah describes the manual process, highlighting its tedious nature. VBrain, developed by Vysioneer, is an AI tool for health care designed to alleviate this burden.
VBrain accelerates the contouring process by approximately 30% on average, and improves contouring accuracy by 12% compared to manual methods. Its FDA-approved deep learning algorithm is capable of detecting the three most prevalent types of brain tumors: metastases, meningiomas, and acoustic neuromas.
Stanford researchers validated VBrain’s efficacy in a study involving 100 patients undergoing stereotactic radiosurgery, a procedure that relies heavily on precise tumor contouring.
“It does 80-90% of the job automatically,” Shah states. “It doesn’t create a materially different outcome, but instead of a human painstakingly drawing something on the image for an hour, they can get it done in 15 minutes.” VBrain significantly reduces the manual workload for radiation oncologists, freeing up valuable time and improving contouring consistency.
5. GI Genius: AI-Powered Polyp Detection During Colonoscopy for Enhanced Cancer Screening
What it is: An AI-powered system that assists in the detection of polyps during colonoscopies.
Who it’s for: Gastroenterologists and endoscopists seeking to improve polyp detection rates and enhance colon cancer screening.
GI Genius, developed by Medtronic, is an FDA-approved AI “back-up camera” designed to aid endoscopists in identifying colon lesions during colonoscopies. This AI tool for health care seamlessly integrates with existing endoscopy equipment and displays in real-time on the endoscopist’s monitor. It automatically identifies suspected polyps and highlights them with green boxes.
Kapoor from Virtua Health describes GI Genius as “like a second set of eyes,” emphasizing its role as a valuable assistant during procedures. He also points to its cost-effectiveness relative to its benefits: “The cost is not prohibitively expensive, but look at the benefit.”
GI Genius is powered by deep learning algorithms that can analyze and interpret unstructured data sets, including endoscopic images. A 2020 study demonstrated that GI Genius increased the adenoma (pre-cancerous polyp) detection rate (ADR) by over 14%. Crucially, colorectal cancer risk decreases by 3% for every 1% increase in ADR. Another study showed that GI Genius analyzed polyps 82% faster than human endoscopists.
An added benefit of GI Genius is its ability to generate a report immediately after the endoscopy procedure. Kapoor notes the positive physician response to this feature: “Doctors love that. It’s less time they have to spend doing documentation.” GI Genius not only improves polyp detection but also streamlines workflow and reduces administrative burden for clinicians.