For professionals and students in public health, mastering epidemiologic and statistical formulas is a core requirement. Initially, these calculations are often performed manually or with basic calculators before transitioning to computer software for efficiency and advanced analysis. While commercial programs like SAS®, SPSS®, and Stata® are widely utilized within schools of public health (SPHs) and are recognized for their robust capabilities in epidemiology, several limitations hinder their accessibility, particularly in resource-constrained environments. These limitations include the high cost of software licenses, the steep learning curve associated with complex interfaces, significant hardware demands, and inconsistent availability of user support.
In response to these challenges, free epidemiologic programs such as Epi Info (www.cdc.gov/epiinfo) and EpiData (www.epidata.dk) have emerged as valuable alternatives. However, even these free options may not encompass the full spectrum of epidemiologic parameters and statistical calculations commonly taught in SPH curricula. Recognizing these gaps, a need was identified for a tool that could effectively support the teaching and application of epidemiologic and statistical procedures, leading to the development of OpenEpi.
Introducing OpenEpi for Public Health Data Analysis
OpenEpi (www.OpenEpi.com) stands out as a robust, free, web-based, and open-source suite of programs specifically designed for public health and medical applications. It serves as an invaluable resource for both training and practical purposes, providing a comprehensive array of epidemiologic and statistical data software tools focused on summary data analysis.2–7 Developed using JavaScript and HTML, OpenEpi is engineered for broad compatibility across various web browsers, including Microsoft® Explorer, Firefox®, Safari, and Opera, and operating systems such as Windows, Macintosh, and Linux. Its versatility extends to mobile platforms, even functioning on devices like iPhones. Users have the flexibility to operate OpenEpi directly from its website or download and run it offline, ensuring accessibility regardless of internet availability. Furthermore, the source code and detailed documentation are readily available for download, encouraging customization and collaborative development within the research community. OpenEpi’s multilingual interface supports users globally, with versions available in English, French, Italian, and Spanish.
The creators of OpenEpi bring extensive expertise from their involvement in developing and rigorously testing Epi Info, a program by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), globally recognized for data entry and analysis in public health. OpenEpi was conceived to replicate and enhance the analytical capabilities of Epi Info’s DOS-based modules, StatCalc and EpiTable, offering a broader spectrum of tools and calculations not originally available in Epi Info. It represents a significant stride towards establishing a fully web-accessible suite of epidemiologic software tools. OpenEpi is envisioned as a complementary tool to Epi Info and other statistical software packages like SAS, SPSS, Stata, and EpiData, with a shared objective of delivering user-friendly data software tools to areas with limited resources.
Initial development of OpenEpi was made possible through a grant from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation to Emory University. Since its launch in 2003, OpenEpi has recorded over 1.4 million accesses from 160 countries, with nearly 500,000 hits in the first half of 2008 alone. A recent Google search highlighted its growing influence, revealing almost 5,000 websites mentioning OpenEpi, underscoring its widespread adoption and recognition within the global health community.
Analytic Capabilities of OpenEpi: A Suite of Data Software Tools
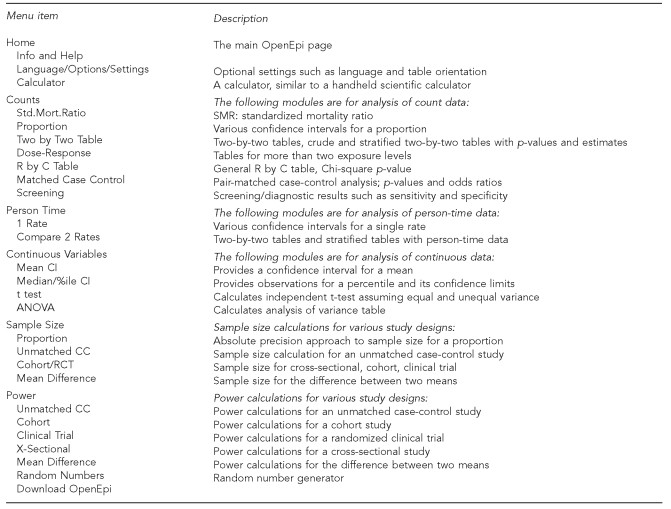
OpenEpi’s analytical capabilities are extensive, covering a wide range of statistical and epidemiologic calculations essential for health care data analysis. Figure 1 provides a visual overview of the modules available within OpenEpi, which encompass:
- Calculation of various confidence intervals tailored for proportions, rates, standard mortality ratios, means, medians, and percentiles, crucial for assessing the precision of health data estimates.
- Two-by-two contingency tables for both crude and stratified data analysis, essential for count and rate data in epidemiologic studies.
- Specialized matched case-control analysis, a critical method in investigating disease outbreaks and risk factors.
- Tests for trend in count data, allowing for the examination of patterns and changes over time in health-related events.
- Independent t-tests and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), standard statistical tools for comparing means across different groups or interventions.
- Diagnostic and screening test analyses, complete with Receiving Operator Characteristic (ROC) curves, essential for evaluating the performance of health screening and diagnostic tools.
- Sample size determination for various study designs including proportions, cross-sectional surveys, unmatched case control, cohort studies, randomized controlled trials, and comparisons of two means, ensuring statistically robust health research.
- Power calculations for proportions (in unmatched case control, cross-sectional, cohort, clinical trials) and for comparisons of two means, vital for effective study design and resource allocation.
- A random number generator, a fundamental utility for simulations and random sampling in research and data analysis.
For epidemiologists and health researchers, OpenEpi enhances data analysis with calculations based on cross-tabulations that are often not standard in other epidemiologic and statistical programs. For a single two-by-two table, beyond the conventional outputs, OpenEpi uniquely estimates:
- Etiologic or prevented fraction in both the population and exposed groups, with confidence intervals, based on risk, odds, or rate data, providing deeper insights into public health impact.
- Both cross-product and maximum likelihood odds ratio estimates, offering comprehensive measures of association.
- Mid-p, exact p-values, and confidence limits for the odds ratio, enhancing the precision of statistical inference.
- Calculations of rate ratios and rate differences with associated confidence intervals and statistical tests, crucial for comparative analysis of health outcomes.
When analyzing stratified two-by-two tables with count data, OpenEpi provides:
- Mantel-Haenszel and precision-based estimates of the risk ratio and odds ratio, essential for controlling confounding in epidemiologic analysis.
- Precision-based adjusted risk difference, offering a refined measure of effect in stratified data.
- Tests for interaction for risk ratio, odds ratio, and risk difference, critical for assessing effect modification.
- Four distinct confidence limit methods for the odds ratio, providing flexibility and robustness in statistical estimation.
Figure 1. OpenEpi menu showcasing its diverse modules and functionalities for health data analysis.
Similar to Epi Info, OpenEpi presents both crude and adjusted estimates in stratified analyses, facilitating the assessment of confounding variables—a key aspect of epidemiological data interpretation. With rate data, OpenEpi calculates adjusted rate ratios and rate differences, and includes tests for interaction to explore effect modification. For count data, OpenEpi also performs tests for trend in both crude and stratified datasets, essential for longitudinal health data analysis.
Figure 2 illustrates the user interface of an OpenEpi module, characterized by five intuitive tabs. The “Start” tab offers a module overview, while the “Enter” tab is dedicated to data input, featuring an “Enter New Data” button for direct data entry. Calculation results are conveniently displayed under the “Results” tab. The “Examples” tab provides a range of pre-loaded examples for learning and practice. A “Help” tab is readily available to address user queries and provide guidance. Furthermore, links to “Documentation” offer detailed analytical methodologies, including the formulas used in each module, and “Testing” sections compare OpenEpi’s outputs against other software and textbook examples, ensuring validation and reliability. Many modules also include a “Load Demo Data” button, streamlining the process of exploring module functionalities with sample datasets.
Figure 2. Example of OpenEpi’s user-friendly interface, demonstrating the “Start” page for a two-by-two table module, designed for ease of use in health data analysis.
OpenEpi as a Teaching Tool in Epidemiology and Public Health
OpenEpi has been effectively integrated as a teaching tool in epidemiology courses at numerous institutions, including Columbia University, Emory University, Morehouse College, San Jose State University, University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, University of Michigan, and University of Wisconsin. Its application spans both campus-based and distance-learning programs. The program’s ease of use, which requires no prior programming expertise, and its web-based accessibility, allows students to concentrate on interpreting results and understanding epidemiologic principles rather than grappling with complex software operations. This makes OpenEpi an ideal data software tool for health care education.
Future Directions for OpenEpi Development
Looking ahead, the developers of OpenEpi are committed to further enhancing its capabilities and expanding its impact in the field of public health. Future development plans include: (1) refining and improving existing programs to enhance user experience and analytical precision; (2) adding new modules to cover a broader spectrum of epidemiologic, statistical, and nutritional calculations, addressing evolving needs in health data analysis; (3) incorporating features to support data interoperability, such as cut-and-paste functionality and the ability to read data from various formats, improving workflow efficiency; (4) expanding language support to translate the program into more languages, broadening its global accessibility; and (5) enhancing global awareness and knowledge of OpenEpi through outreach and training initiatives. Prototype modules, including logistic regression and survival analysis, are currently accessible at http://www.sph.emory.edu/∼cdckms, signaling ongoing advancements. The OpenEpi team actively encourages contributions from the wider community to develop and test new modules, fostering a collaborative approach to expanding the utility of this valuable public health resource.